Investors aiming for strong returns are always watching for neighborhoods where the market isn’t just performing—it’s outperforming expectations. In 2025, the Golden Rule remains: buy smart, based on data and community strength. Here’s a refined look at the areas delivering standout ROI (Return on Investment) today.
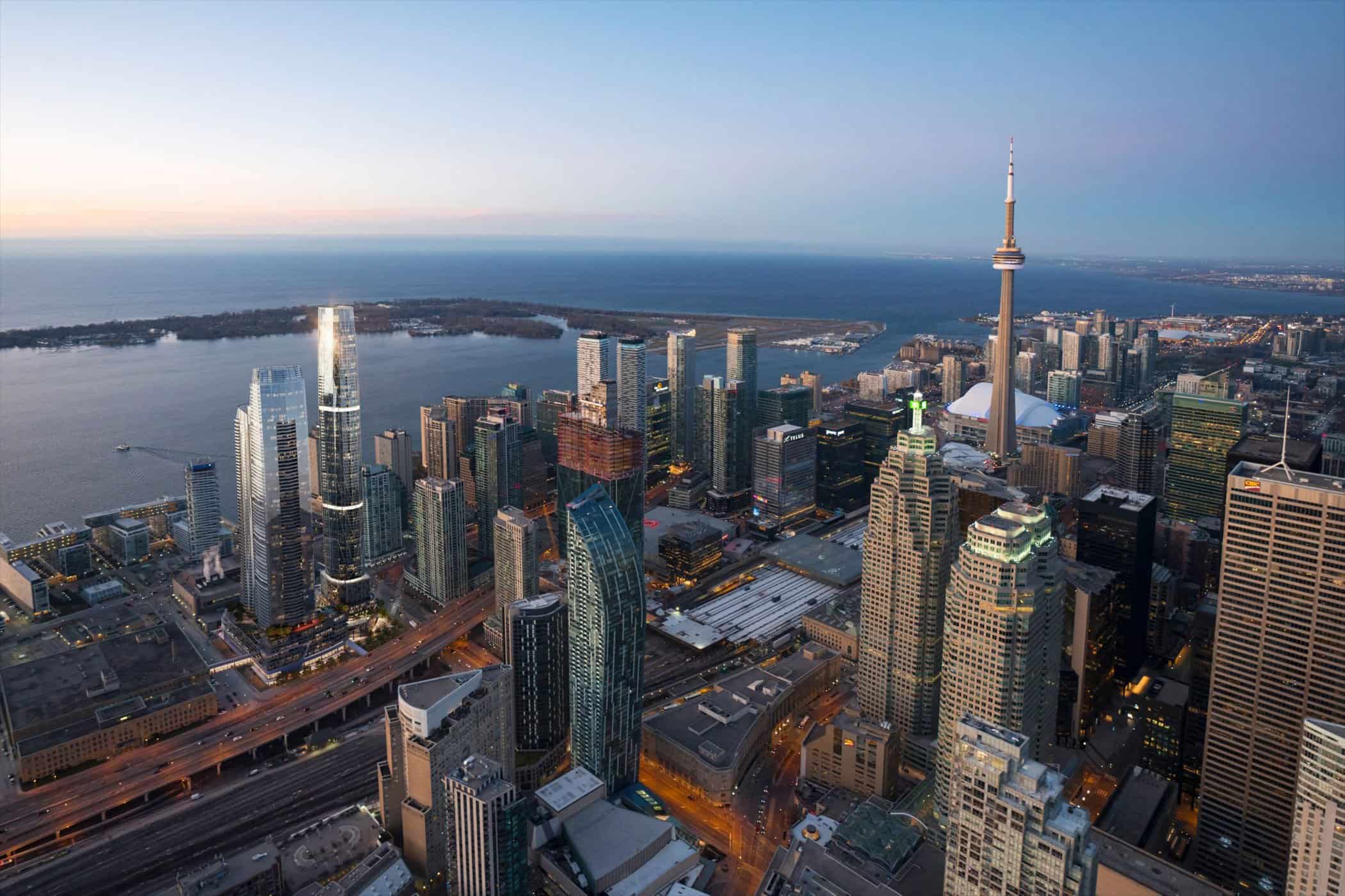
1. Toronto & the Greater Toronto Area (GTA): Still the Gold Standard
Toronto continues to lead Ontario’s investment scene. With a robust job market, steady immigration, and high rental demand—from students to professionals—the GTA remains the cornerstone. Average semi-detached home prices hover near C$950,000, buoyed by consistent demand.
2. Barrie: Affordable Growth on the Rise
Just north of the GTA, Barrie offers properties at a lower price point but with growing buyer and renter interest. In 2024, home prices jumped roughly 12%, making it a magnet for investors seeking appreciation and rental yield.
3. Kitchener-Waterloo: Tech-Driven Momentum
Canada’s budding "Silicon Valley," Kitchener-Waterloo, remains hot thanks to its tech sector boom and universities. Strong employment and rental demand make this a high-performing real estate pick.
4. Hamilton: The Unexpected Power Player
Hamilton is no longer just “affordable Toronto.” With revitalization projects and steady demand from commuters, appreciation rates near 10% signal smart upward momentum.
5. Guelph: Stability + Student Demand
Guelph balances affordability, low unemployment, and institutional rental demand—especially from its university. It’s a smart pick for low-risk, steady returns.
Final Summary
For investors in 2025 seeking ROI, targeting cities with affordability plus demand is key. Greater Toronto continues to anchor value, while Barrie, Hamilton, Kitchener-Waterloo, and Guelph offer scalable, high-upside alternatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where do most millionaires live in Toronto?
Elite neighborhoods include Bridle Path (the famed "Millionaires' Row"), Forest Hill, Rosedale, Lawrence Park, and Casa Loma.
Is Toronto a good place to invest in property?
Absolutely. As Ontario’s economic hub, Toronto offers high demand, strong job growth, and consistent population inflows—making it one of the most stable and active real estate markets in the province.
Where is the best place in Ontario to invest in real estate?
Top-performing Ontario markets in 2025 include:
Toronto/GTA – anchored by demand.
Barrie – strong appreciation.
Kitchener-Waterloo – tech-driven growth.
Hamilton – affordable with upward momentum.
Guelph – stable student rental demand.
What is the best neighborhood to live in Toronto?
For family comfort, schools, and prestige, neighborhoods like Rosedale, Forest Hill, Lawrence Park, and Leaside rank among the city’s best living experiences.
What income is considered rich in Toronto?
Top 10% individual earners in Toronto make around C$130,100, and median individual income is about C$40,300. To qualify for an average Toronto home, households often need upward of C$195,000–$200,000 annually.





.png)








